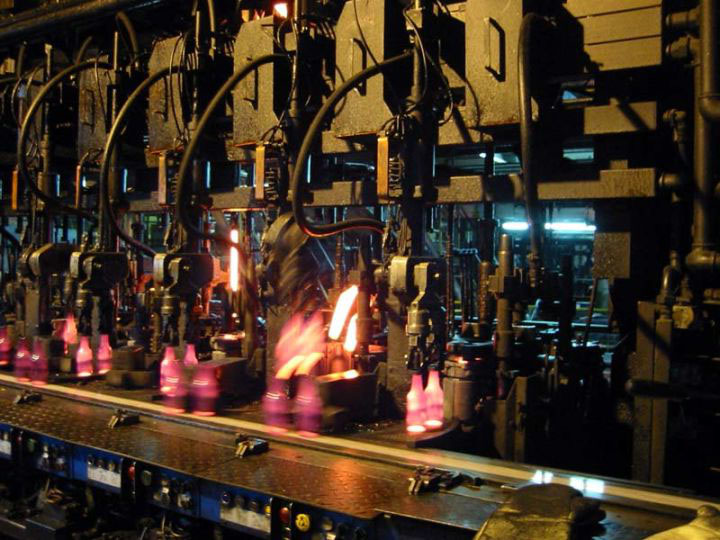
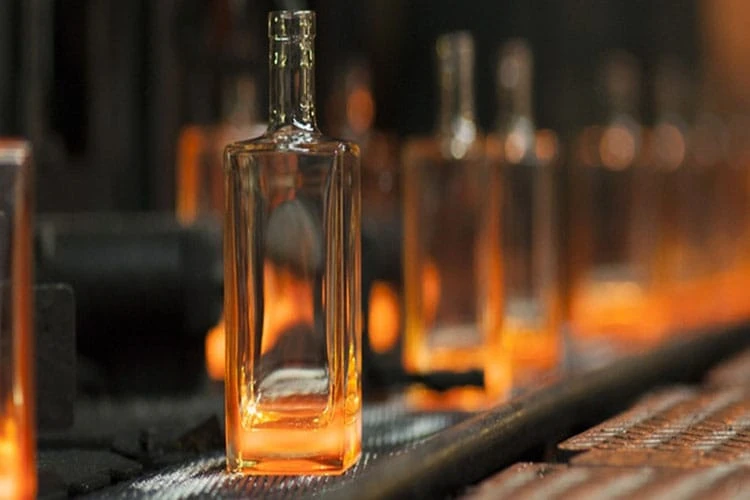
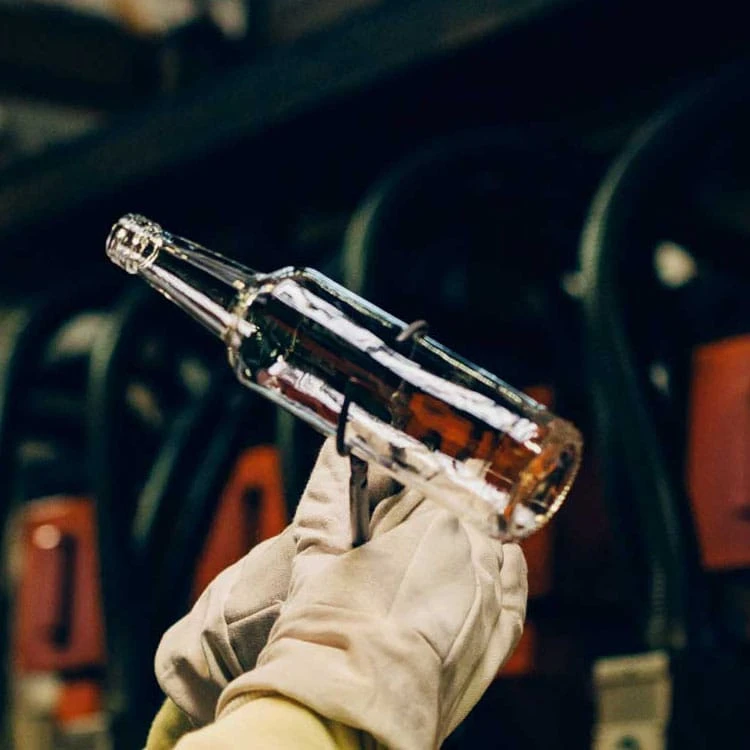
The bottle spraying method in glass wine bottle production is a critical process that ensures high-quality finishes and durability. This production line typically consists of several key components: the spraying room, hanging chain, and oven. Additionally, effective water treatment for glass bottles is essential, particularly regarding sewage discharge management.
Factors Influencing Glass Bottle Spraying Quality
The quality of glass bottle spraying is influenced by several factors, including:
Water Treatment: Proper treatment is vital for achieving a clean surface on the glass bottles.
Surface Cleaning: Ensuring that workpieces are free of contaminants is crucial for adhesion.
Conductivity of Hooks: This affects the electrostatic spraying process.
Air Volume and Powder Amount: These parameters must be carefully calibrated to ensure even coating.
Operator Skill Level: Experienced operators can significantly improve the efficiency and quality of the spraying process.
Recommended Methods for Bottle Spraying
To achieve optimal results, consider implementing the following methods during the different stages of the spraying process:
1. Pretreatment Stage
The pretreatment phase includes several steps: pre stripping, main stripping, and surface conditioning. In colder weather, it’s important to maintain the temperature of the main stripping section to ensure effective treatment; otherwise, the results may be subpar.
2. Preheating Stage
After pretreatment, glass bottles enter the preheating section, which typically lasts 8 to 10 minutes. This step is crucial because it allows the bottles to retain some waste heat before entering the powder spraying chamber, enhancing the adhesion of the powder.
3. Soot Blowing and Purification Stage
For workpieces requiring high-quality finishes, this stage is essential. If dust accumulates on the surface, it can lead to particle contamination, negatively impacting the quality of the finished product. Ensuring a clean environment during this stage is vital.
4. Spraying Stage
Glass bottles are traditional and widely used packaging containers. Despite the rise of various packaging materials, glass remains a preferred option due to its unique properties. During the spraying stage, it’s crucial to achieve an even coat of raw materials while maintaining consistent thickness across the surface.
5. Drying Stage
Finally, the drying stage requires careful attention to both temperature and baking time. Typically, the baking temperature should range from 180 to 200 °C, depending on the specific materials being used.
Conclusion
The spraying method used by glass bottle manufacturers plays a vital role in producing high-quality glass wine bottles. By focusing on each stage of the process—from pretreatment to drying—manufacturers can ensure that their products meet the highest standards of quality and performance.
If you’re looking for more knowledge of glass bottles, check out the following articles:
– Top 4 Drinking Glass Manufacturers in the U.S
– Everything You Need to Know About Liquor Bottle Sizes
– Why Choose Apple Juice in Small Glass Bottles? A Flavorful Experience
Consult Your Valiant Glass Bottles & Packaging Experts
We help you avoid the pitfalls to deliver the quality and value your glass bottle and jar need, on-time and on-budget.